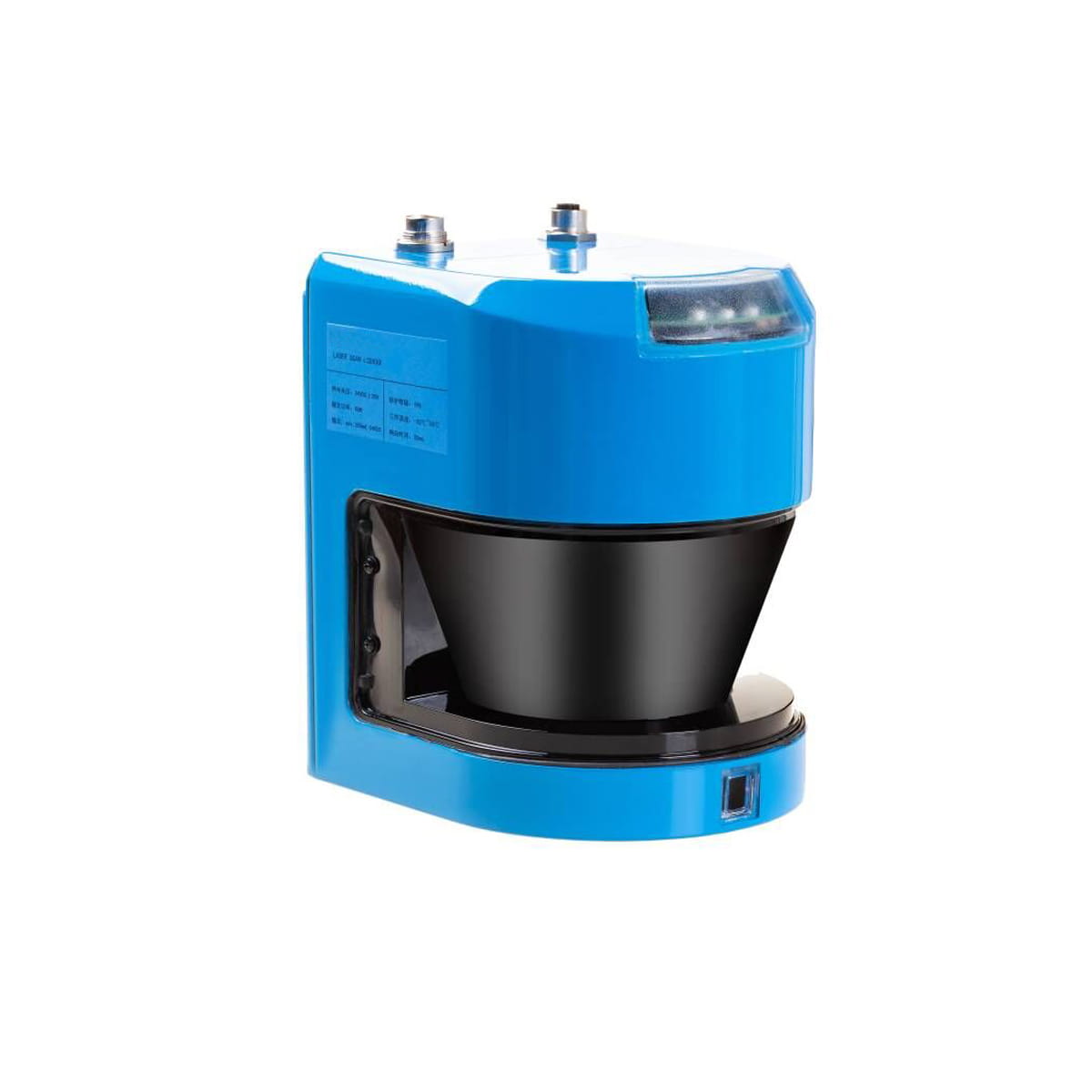
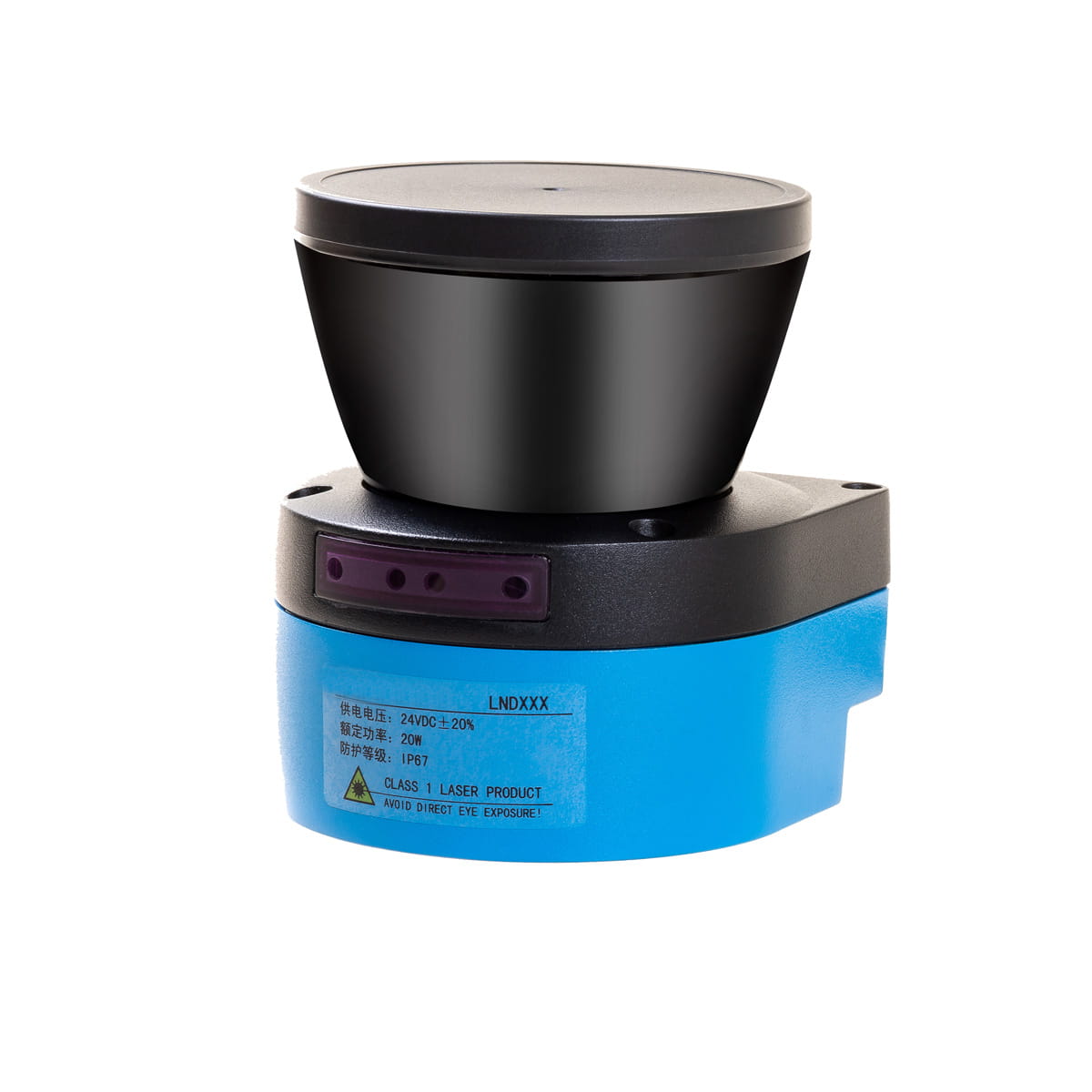
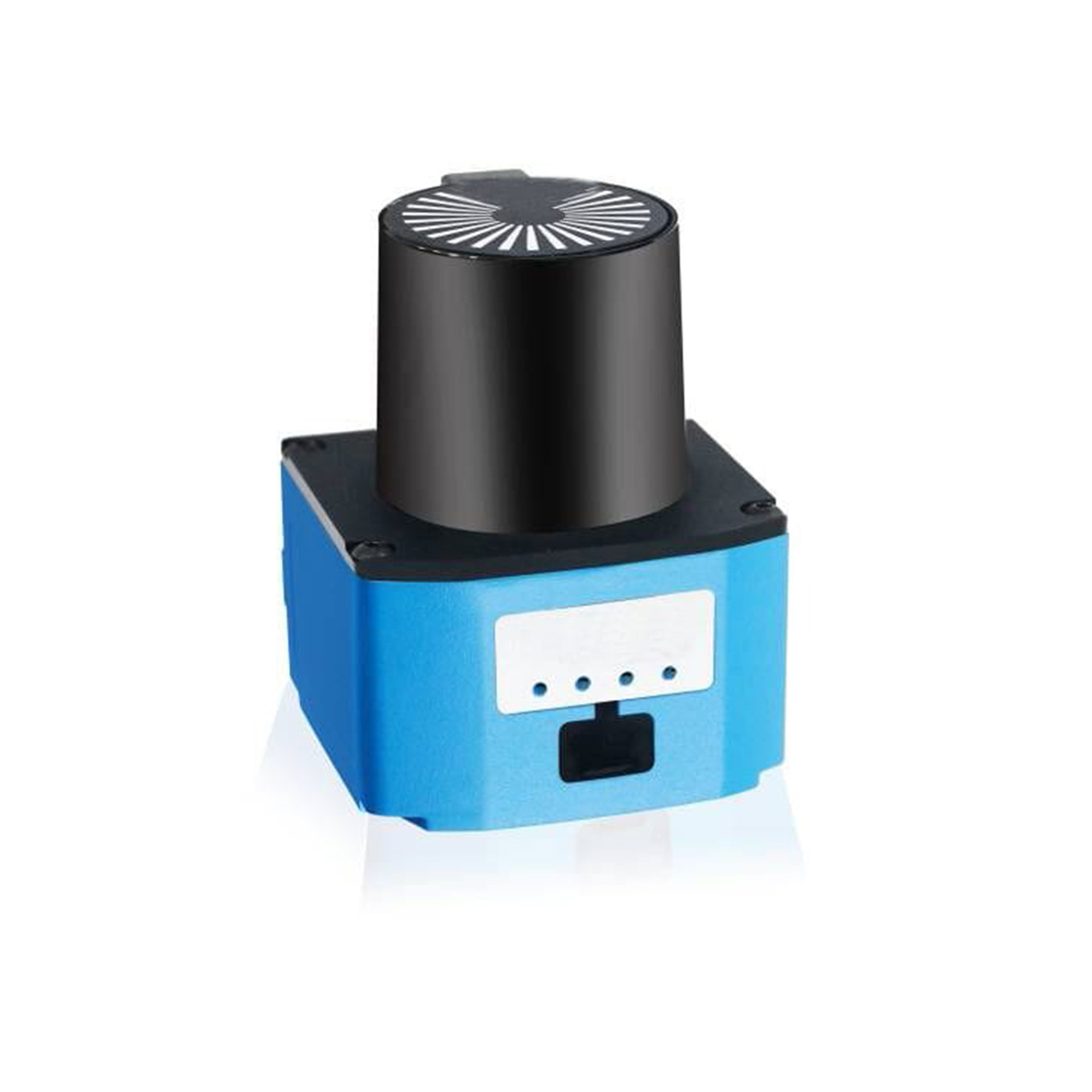
Lidar is classified in different ways according to the difference of ranging mode and scanning harness.
Lidar is divided into two types according to the ranging principle: triangular ranging and time of flight (TOF) ranging. The time-of-flight ranging includes direct time of flight (dTOF) and indirect time of flight (iTOF).
The principle of triangulation method is that the laser is emitted by the laser scanner. After the laser irradiates the object, the reflected light is received by the linear CCD. Because the laser and the detector are separated by a certain distance, according to the optical path, objects at different distances will be imaged at different positions on the CCD. According to the trigonometric formula, the distance of the measured object can be derived.
The principle of TOF is that the laser emits a laser pulse, and the timer records the outgoing time. The return light is received by the receiver, and the timer records the return time. The “flight time” of light is obtained by subtracting the two times, and the speed of light is certain, so it is easy to calculate the distance after the speed and time are known. Compared with the triangular ranging method, TOF calculates the target distance by measuring the flight time of the optical pulse, and the timing accuracy will not change due to the distance, so the range resolution of TOF ranging will not change substantially in the whole range. At the same time, TOF ranging processes high-speed pulse signals, which has the advantage that the whole measurement process is extremely time-consuming and can easily achieve a very high measurement frequency.
According to whether there are mechanical rotating parts inside the laser radar sensor, lidar can be divided into three types: mechanical, solid and mixed solid.
Mechanical lidar is a mechanical scheme that drives the overall rotation of the optical and mechanical structure through the motor. The laser pulse transmitter, receiver and other components will rotate 360 ° with the scanning module, so as to generate a three-dimensional point cloud to realize the perceptual scanning of the environment.
Compared with mechanical lidar, solid-state lidar only scans at a certain angle in one direction, and its coverage is limited. However, the mechanical structure with complex high-frequency rotation has been eliminated, the durability has been greatly improved, and the volume can also be greatly reduced.
The hybrid solid-state radar does not need to rotate the laser transmitter and receiver through the mechanical structure for 360 degree scanning. It is small in size and low in cost, but there are some small mechanical moving parts inside.